
Yi-Guang Chen, PhD
Professor, Pediatrics (Endocrinology) and Microbiology & Immunology
Locations
- Pediatrics (Endocrinology)
TBRC C2520
Contact Information
General Interests
Education
BS, National Taiwan University, Taiwan, 1993
Research Interests
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) results from T cell mediated destruction of insulin producing pancreatic β-cells. Although T1D is most frequently diagnosed in children and young adults, it is a life-long disease requiring daily injections or infusions of exogenous insulin to maintain glucose homeostasis. Furthermore, many T1D patients develop diabetic complications later in life significantly threatening the quality of their lives. Unfortunately, the incidence of T1D has been increasing worldwide in the past decades. Studies conducted in both rodent models and humans indicate that genetic susceptibility significantly contributes to T1D development. Human genome wide association studies (GWAS) have identified more than 50 loci significantly linked to T1D. However, our knowledge of the underlying genes within the mapped GWAS regions and their pathogenic roles in T1D is incomplete. The focus of our research program is to further understand the genetic basis of T1D with the following three main goals. (1) To identify T1D susceptibility genes and mechanistically study their disease modulating functions, (2) To evaluate the potential of pharmaceutical targeting of T1D susceptibility genes and the pathways in which they are involved for disease prevention and reversal, and (3) To determine if T1D susceptibility genes also modulate the responses to clinically relevant therapeutic agents. The NOD mouse represents one of the best rodent models for T1D research. NOD mice develop spontaneous T1D with characteristics similar to the human disease. Our current effort is to genetically modify genes within the human T1D susceptibility loci identified by GWAS in NOD mice and functionally evaluate their roles in diabetes development. These genetically modified NOD mice also allow us to study how T1D susceptibility genes contribute to diabetes development at both the molecular and cellular levels.
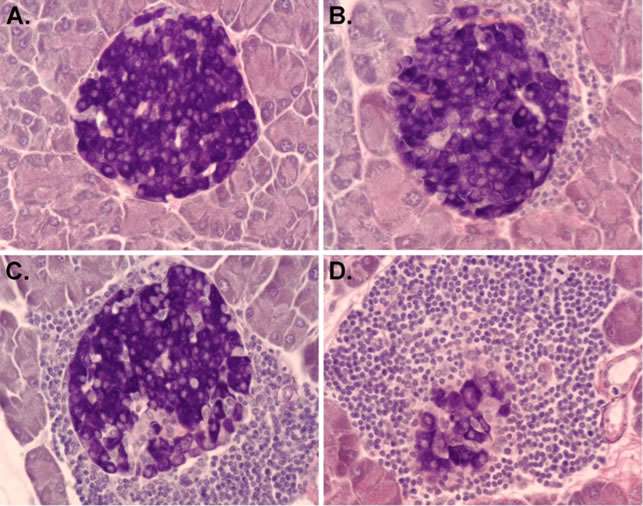
Figure 1. Islet infiltration of leukocytes that destroy pancreatic β-cells in NOD mice. (A) A healthy islet without leukocyte infiltration. (B-D) Islets with various levels of leukocyte infiltration (insulitis).
Publications
-
Alternate splicing converts human CD137 from costimulatory to immunosuppressive function.
(Rojas M, Heuer LS, Zhang W, Sweeney N, Ramírez-Santana C, Leung PSC, Lam A, Kamat S, Mendelsohn AR, Huang M, Yu B, Ackerman P, Wei Q, Larrick JW, Chen YG, Ridgway WM.) J Autoimmun. 2025 Dec;157:103498 PMID: 41205341 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-105020876359 11/09/2025
-
(Ciecko AE, Nabi R, Drewek A, Schauder DM, Zakharov PN, Wan X, Lieberman SM, Cui W, Hessner MJ, Lin CW, Chen YG.) iScience. 2025 Oct 17;28(10):113537 PMID: 41050931 PMCID: PMC12494592 10/06/2025
-
(Juan W, Ahn KW, Chen YG, Lin CW.) Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jul 31;12(8) PMID: 40868342 PMCID: PMC12383624 08/30/2025
-
A realistic FastQ-based framework FastQDesign for ScRNA-seq study design issues.
(Wang Y, Chen YG, Ahn KW, Lin CW.) Commun Biol. 2025 Apr 02;8(1):547 PMID: 40175506 PMCID: PMC11965523 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-105001734248 04/03/2025
-
CCI: A Consensus Clustering-Based Imputation Method for Addressing Dropout Events in scRNA-Seq Data.
(Juan W, Ahn KW, Chen YG, Lin CW.) Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jan 03;12(1) PMID: 39851305 PMCID: PMC11763284 01/24/2025
-
(Ciecko AE, Nabi R, Drewek A, Schauder DM, Zakharov PN, Wan X, Lieberman SM, Cui W, Hessner MJ, Lin CW, Chen YG.) Iscience. 17 October 2025;28(10) SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-105016644538 10/17/2025
-
(Srivastava N, Hu H, Peterson OJ, Vomund AN, Stremska M, Zaman M, Giri S, Li T, Lichti CF, Zakharov PN, Zhang B, Abumrad NA, Chen YG, Ravichandran KS, Unanue ER, Wan X.) Immunity. 2024 Jul 09;57(7):1629-1647.e8 PMID: 38754432 PMCID: PMC11236520 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85194456425 05/17/2024
-
IL-27 promotes pathogenic T cells in a mouse model of Sjögren's disease.
(Debreceni IL, Barr JY, Upton EM, Chen YG, Lieberman SM.) Clin Immunol. 2024 Jul;264:110260 PMID: 38788885 PMCID: PMC11203157 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85193848203 05/25/2024
-
(Pant T, Lin CW, Bedrat A, Jia S, Roethle MF, Truchan NA, Ciecko AE, Chen YG, Hessner MJ.) Sci Adv. 2024 May 17;10(20):eadn2136 PMID: 38758799 PMCID: PMC11100571 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85193631768 05/17/2024
-
IL-13 promotes functional recovery after myocardial infarction via direct signaling to macrophages.
(Alvarez-Argote S, Paddock SJ, Flinn MA, Moreno CW, Knas MC, Almeida VA, Buday SL, Bakhshian Nik A, Patterson M, Chen YG, Lin CW, O'Meara CC.) JCI Insight. 2024 Jan 23;9(2) PMID: 38051583 PMCID: PMC10906228 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85183312687 12/06/2023
-
(Ye C, Clements SA, Gu W, Geurts AM, Mathews CE, Serreze DV, Chen YG, Driver JP.) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 05;120(49):e2312039120 PMID: 38015847 PMCID: PMC10710095 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85178500431 11/28/2023
-
(Thirawatananond P, Brown ME, Sachs LK, Arnoletti JM, Yeh WI, Posgai AL, Shapiro MR, Chen YG, Brusko TM.) Diabetes. 2023 Nov 01;72(11):1629-1640 PMID: 37625150 PMCID: PMC10588280 SCOPUS ID: 2-s2.0-85175068629 08/25/2023

